Environment
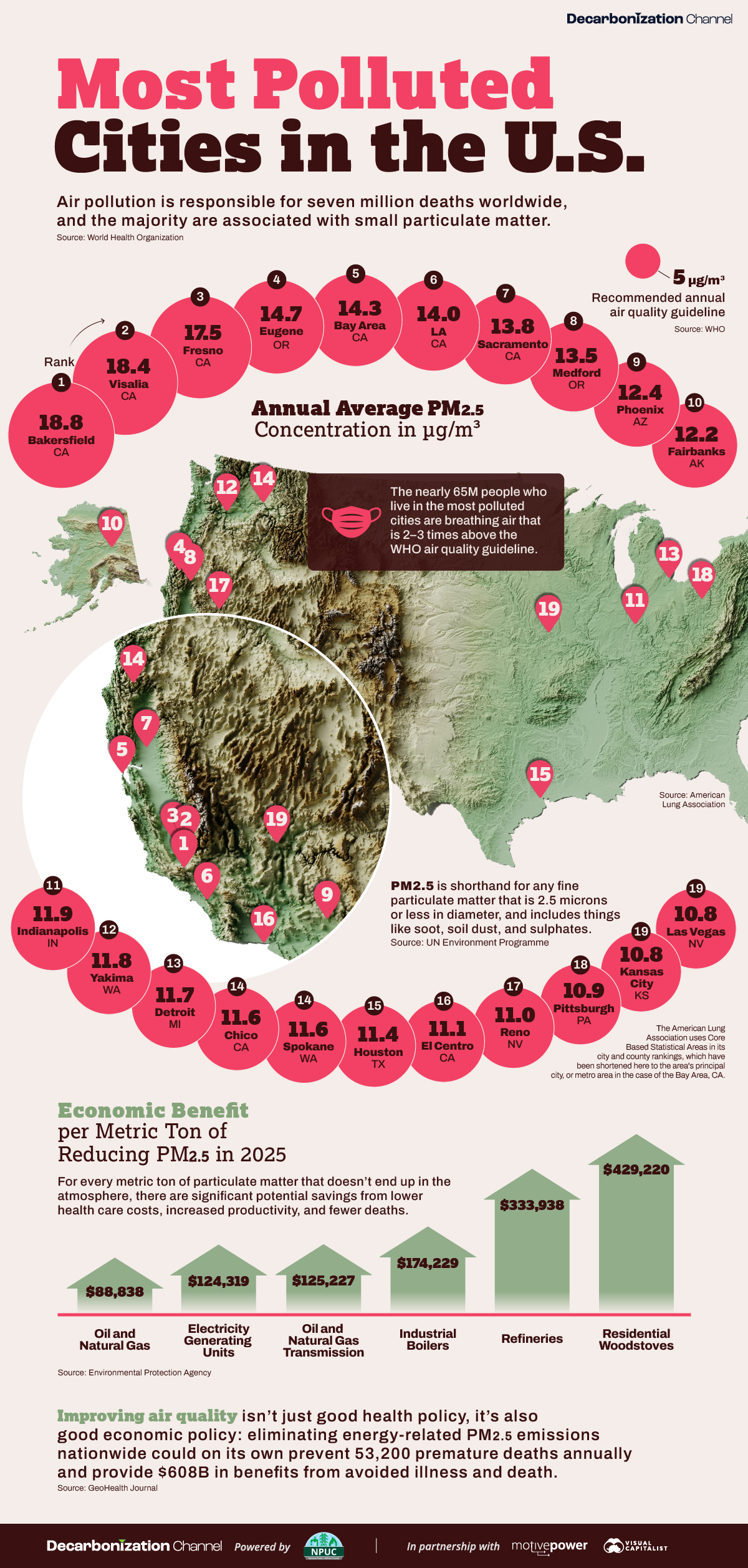
Ranked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
![]() See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
Ranked: Top Countries By Total Forest Loss Since 2001
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Forests are critical natural resources, often caught in the crosshairs of economic development. Thanks to expanding human settlement, agriculture, and industry, the world lost nearly 1 million square kilometers (km²) of forest cover since 2001.
But where has most of this deforestation occurred?
We rank the countries by the total decrease in their forest area between 2001 and 2021, measured in square kilometers along with their percentage decrease for context. All of this data was sourced from the World Bank.
A caveat to this data: countries are ranked by total forest loss, so countries with the largest forests feature predominantly on this list.
Which Country Has Lost the Most Forests (2001-2021)?
Brazil has lost more than half a million square kilometers of forest in the last two decades. Agricultural expansion for beef and soy production alongside mining and infrastructure growth are the primary drivers behind this large scale deforestation.
This has also caused periodic fires in the Amazon rainforest, drawing repeated alarm from around the world. In fact, Brazil has lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
The table below lists the countries included in this graphic, as well as several others further down the ranking.
| Rank | Country | Region | 2001–21 Change (in km2) | % of Forest Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | South America | -517,464 | -9% |
| 2 | 🇨🇩 DRC | Africa | -181,721 | -13% |
| 3 | 🇦🇴 Angola | Africa | -111,012 | -14% |
| 4 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | Africa | -106,213 | -37% |
| 5 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | Asia | -95,903 | -9% |
| 6 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | Africa | -80,220 | -15% |
| 7 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | South America | -68,266 | -30% |
| 8 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | Asia | -62,712 | -18% |
| 9 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | South America | -45,979 | -14% |
| 10 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | Africa | -44,688 | -11% |
| 11 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | South America | -42,791 | -8% |
| 12 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | South America | -36,001 | -6% |
| 13 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | Africa | -32,661 | -13% |
| 14 | 🇵🇪 Peru | South America | -30,155 | -4% |
| 15 | 🇰🇭 Cambodia | Asia | -28,491 | -26% |
| 16 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | South America | -28,130 | -6% |
| 17 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | North America | -26,732 | -4% |
| 18 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | Africa | -23,924 | -5% |
| 19 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | Africa | -23,660 | -14% |
| 20 | 🇨🇮 Cote d'Ivoire | Africa | -22,577 | -45% |
What is quickly apparent is how most of the countries on this list are from Africa and South America. A study found a correlation where developing economies tend to have higher deforestation rates than advanced economies. Former colonies have also experienced more forest loss than those that were not colonized.
In Asia, Indonesia’s burgeoning palm oil industry is a key driver to deforestation, though efforts are now being made to reverse its impact. Meanwhile, Cambodia experienced rapid clear-cutting for its growing rubber plantations and timber industry.
Finally, Myanmar has long contended with illegal logging, but the country’s ongoing civil war is styming conversation efforts.
Environment
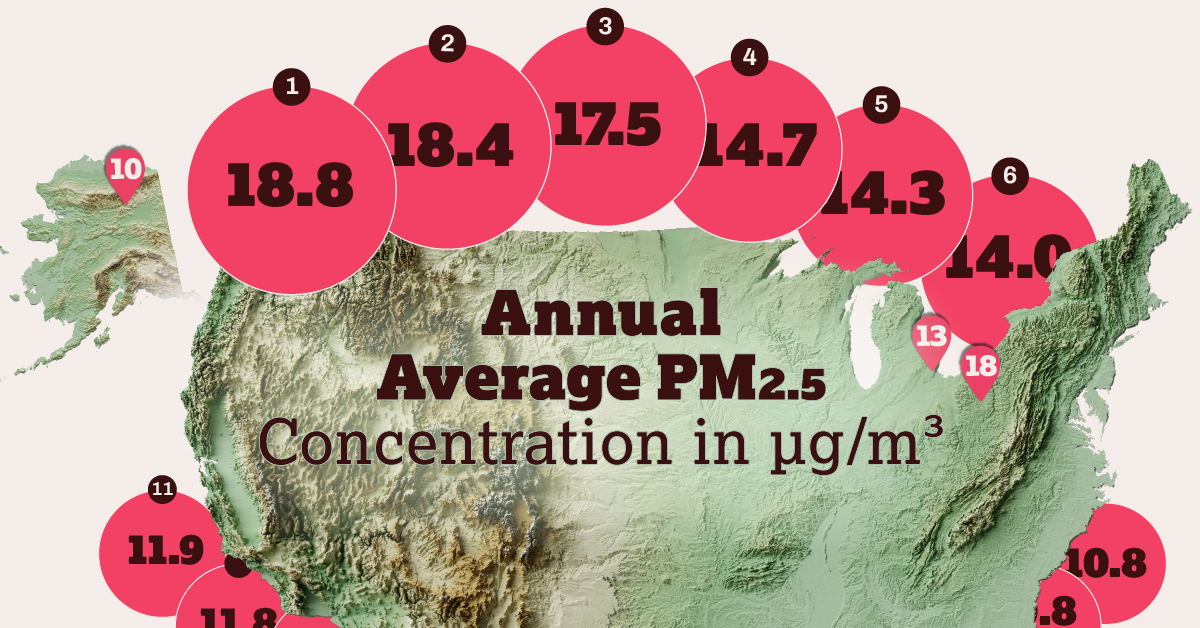
The Most Polluted Cities in the U.S.
What are the most polluted cities in the U.S. according to data from the American Lung Association’s 2024 State of the Air Report?
The Most Polluted U.S. Cities in 2024
According to the World Health Organization, air pollution is responsible for 7 million deaths annually, and could cost the global economy between $18–25 trillion by 2060 in annual welfare costs, or roughly 4–6% of world GDP.
And with predictions that 7 in 10 people will make their homes in urban centers by mid-century, cities are fast becoming one of the frontlines in the global effort to clear the air.
In this visualization, we use 2024 data from the State of the Air report from the American Lung Association to show the most polluted cities in the United States.
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution is a complex mixture of gases, particles, and liquid droplets and can have a variety of sources, including wildfires and cookstoves in rural areas, and road dust and diesel exhaust in cities.
There are a few kinds of air pollution that are especially bad for human health, including ozone and carbon monoxide, but here we’re concerned with fine particulate matter that is smaller than 2.5 microns, or PM2.5 for short.
The reason for the focus is because at that small size, particulate matter can penetrate the bloodstream and cause all manner of havoc, including cardiovascular disease, lung cancer, and chronic pulmonary disease.
The American Lung Association has set an annual average guideline of 9 µg/m³ for PM2.5, however, the World Health Organization has set a much more stringent limit of 5 µg/m³.
The 21 Worst Polluted Cities in the U.S.
Here are the top 21 most polluted cities in the U.S., according to their annual average PM2.5 concentrations:
| Rank | City, State | Annual average concentration, 2020-2022 (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bakersfield, CA | 18.8 |
| 2 | Visalia, CA | 18.4 |
| 3 | Fresno, CA | 17.5 |
| 4 | Eugene, OR | 14.7 |
| 5 | Bay Area, CA | 14.3 |
| 6 | Los Angeles, CA | 14.0 |
| 7 | Sacramento, CA | 13.8 |
| 8 | Medford, OR | 13.5 |
| 9 | Phoenix, AZ | 12.4 |
| 10 | Fairbanks, AK | 12.2 |
| 11 | Indianapolis, IN | 11.9 |
| 12 | Yakima, WA | 11.8 |
| 13 | Detroit, MI | 11.7 |
| T14 | Chico, CA | 11.6 |
| T14 | Spokane, WA | 11.6 |
| 15 | Houston, TX | 11.4 |
| 16 | El Centro, CA | 11.1 |
| 17 | Reno, NV | 11.0 |
| 18 | Pittsburgh, PA | 10.9 |
| T19 | Kansas City, KS | 10.8 |
| T19 | Las Vegas, NV | 10.8 |
Note: The American Lung Association uses Core Based Statistical Areas in its city and county rankings, which have been shortened here to the area’s principal city, or metro area in the case of the Bay Area, CA.
Six of the top seven cities are in California, and four in the state’s Central Valley, a 450-mile flat valley that runs parallel to the Pacific coast, and bordered by the Coast and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges. As a result, when pollution from the big population centers on the coast is carried inland by the wind—cities #5 and #6 on the list—it tends to get trapped in the valley.
Bakersfield (#1), Visalia (#2), and Fresno (#3) are located at the drier and hotter southern end of the valley, which is worse for air quality. The top three local sources of PM2.5 emissions in 2023 were farms (20%), forest management / agricultural waste burning (20%), and road dust (14%).
Benefit to Economy
While the health impacts are generally well understood, less well known are the economic impacts.
Low air quality negatively affects worker productivity, increases absenteeism, and adds both direct and indirect health care costs. But the flip side of that equation is that improving air quality has measurable impacts to the wider economy. The EPA published a study that calculated the economic benefits of each metric ton of particulate matter that didn’t end up in the atmosphere, broken down by sector.
| Sector | Benefits per metric ton |
|---|---|
| Residential Woodstoves | $429,220 |
| Refineries | $333,938 |
| Industrial Boilers | $174,229 |
| Oil and Natural Gas Transmission | $125,227 |
| Electricity Generating Units | $124,319 |
| Oil and Natural Gas | $88,838 |
At the same time, the EPA recently updated a cost-benefit analysis of the Clean Air Act, the main piece of federal legislation governing air quality, and found that between 1990 and 2020 it cost the economy roughly $65 billion, but also provided $2 trillion in benefits.
Benefit to Business
But that’s at the macroeconomic level, so what about for individual businesses?
For one, employees like to breathe clean air and will choose to work somewhere else, given a choice. A 2022 Deloitte case study revealed that nearly 70% of highly-skilled workers said air quality was a significant factor in choosing which city to live and work in.
At the same time, air quality can impact employer-sponsored health care premiums, by reducing the overall health of the risk pool. And since insurance premiums averaged $7,590 per year in 2022 for a single employee, and rose to $21,931 for a family, that can add up fast.
Consumers are also putting their purchase decisions through a green lens, while ESG, triple-bottom-line, and impact investing are putting the environment front and center for many investors.
And if the carrot isn’t enough for some businesses, there is the stick. The EPA recently gave vehicle engine manufacturer Cummins nearly two billion reasons to help improve air quality, in a settlement the agency is calling “the largest civil penalty in the history of the Clean Air Act and the second largest environmental penalty ever.”

Learn how the National Public Utilities Council is working toward the future of sustainable electricity.

-

 Environment1 month ago
Environment1 month agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
The country with the most forest loss since 2001 lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
-

 Environment3 months ago
Environment3 months agoCharted: Share of World Forests by Country
We visualize which countries have the biggest share of world forests by area—and while country size plays a factor, so too, does the environment.
-
 Green4 months ago
Green4 months agoWhich Countries Have the Largest Forests?
Together, the top five countries with the largest forests account for more than half of the world’s entire forest cover.
-
 Healthcare5 months ago
Healthcare5 months agoVisualized: What Lives in Your Gut Microbiome?
The human gut microbiome contains a world of microbes. We look at the the bacteria that deeply affect our health and well-being.
-

 Green5 months ago
Green5 months agoMapped: Global Temperature Rise by Country (2022-2100P)
In this set of three maps, we show the global temperature rise on a national level for 2022, 2050, and 2100 based on an analysis by…
-
 Green5 months ago
Green5 months agoRanked: Per Capita Carbon Emissions by Country
Which countries rank the highest in per capita carbon emissions, and how do they impact the world’s total carbon emissions?
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State
-
 Misc6 days ago
Misc6 days agoVisualized: Aircraft Carriers by Country
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoHow Popular Snack Brand Logos Have Changed
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
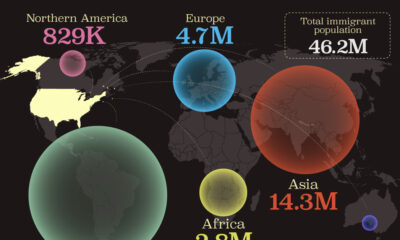
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Maps1 week ago
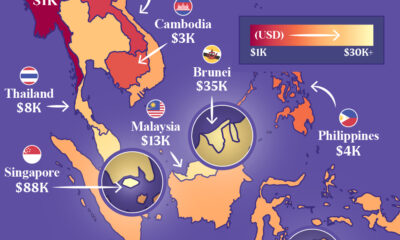
Maps1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country